In recent years, the quick commerce landscape in India has been undergoing a massive transformation. Blinkit, formerly known as Grofers, is one of the key players in the emerging quick commerce sector.
According to a 2025 Bain & Company report, over two-thirds of all e-grocery orders and 10% of e-retail spending occurred on Q-commerce platforms. Around 70% of Gen Z shoppers in India find brands online and make impulse purchasing decisions, often browsing fewer search results than millennials before making a purchase.
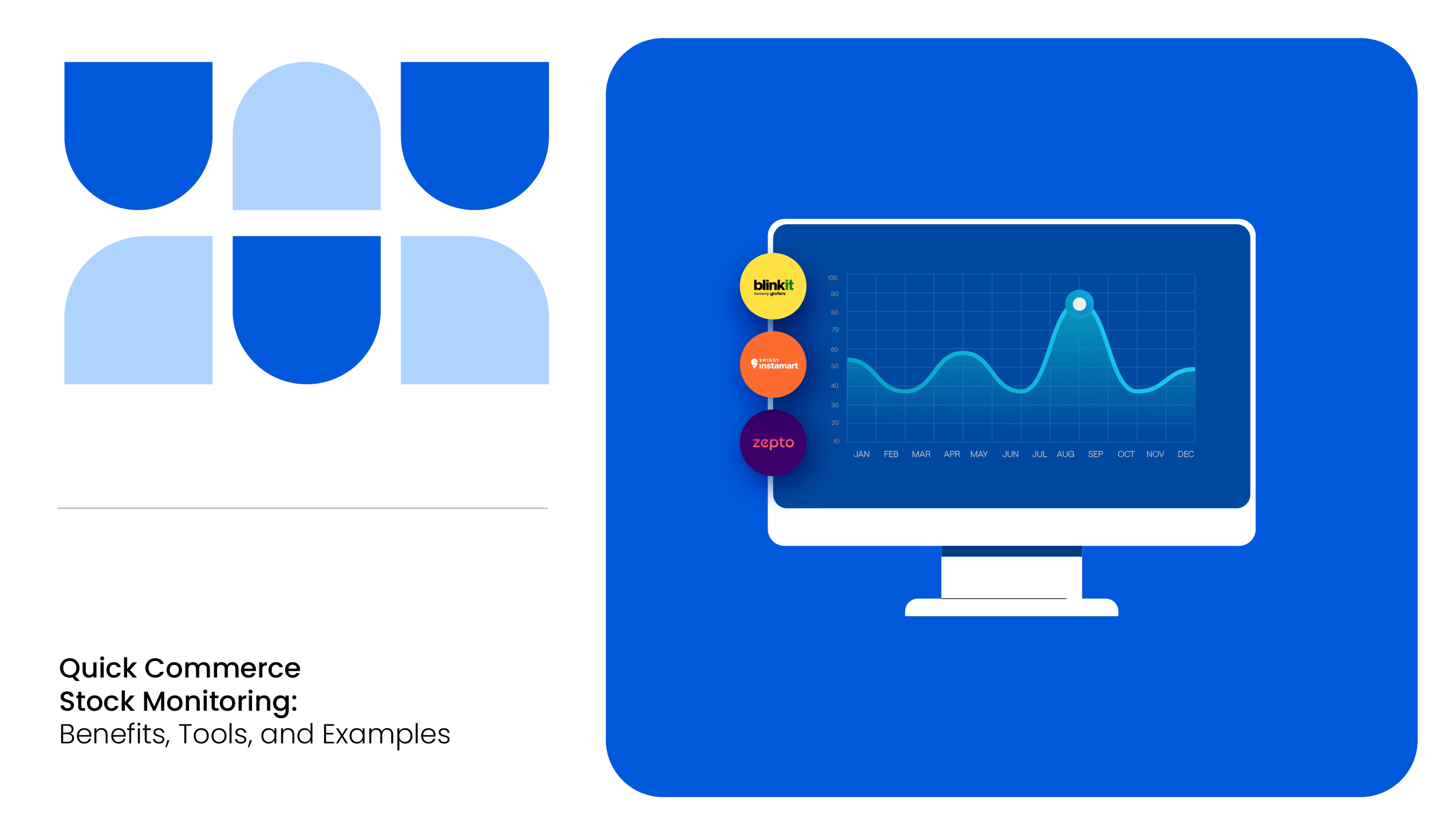
MetricsCart equips brands with real-time insights that are essential for thriving in the fast-paced world of quick commerce. In a space where every second and every SKU matters, this quick commerce intelligence tool ensures your products stay competitive, discoverable, and conversion-ready.
Introduction to Blinkit
Launched in 2013 by Albinder Dhindsa and Saurabh Kumar, Blinkit initially began as a grocery delivery platform under the name “Grofers.” Over the years, it evolved and became synonymous with rapid, on-demand deliveries.
In 2021, the company rebranded to Blinkit to reflect its shift toward quick commerce, emphasizing its focus on speed, convenience, and an ultra-fast delivery service.
With over 7,000 products available, including groceries, electronics, beauty products, and home essentials, Blinkit aims to deliver all of this in as little as 10 minutes.
READ MORE | Want to know how impulse purchasing decisions help retailers? Check out our blog on Online Impulse Buying: Reasons and How Retailers Can Incentivize.
The Blinkit Business Model: A Hyper-Local Approach to E-Commerce
Blinkit operates on a hyper-local marketplace model that connects consumers with local vendors. It utilizes dark stores and fast delivery to cater to the growing demand for convenience.
India’s distinct demographic landscape is characterized by a large population of price-sensitive consumers, especially those in the 25 to 34 age group, who are highly engaged in social media. This makes it an ideal environment for the trend-driven quick commerce boom.
As the influencer and supplier ecosystems continue to grow rapidly, this momentum is expected to drive even more tremendous growth in the sector.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components of Blinkit’s business model:

Hyper-Local Inventory Model
At the heart of Blinkit’s business model is its hyper-local inventory system. Unlike traditional e-commerce platforms that maintain large, centralized warehouses, Blinkit relies on a network of dark stores and small, strategically located warehouses within cities that are stocked with high-demand products. These dark stores are typically located in residential areas to ensure that products are always close to consumers.
This local inventory system allows Blinkit to drastically reduce delivery times, ensuring that products are available for delivery within 10-30 minutes. It enables the platform to keep operational costs low and deliver items quickly without having to rely on long-distance shipping or bulky warehouses.
The Blinkit Delivery Model
One of Blinkit’s unique selling points is its delivery model. The company partners with independent delivery personnel (also known as delivery agents) who pick up orders directly from the dark stores and deliver them to customers. The delivery agents are equipped with real-time tracking tools to help ensure smooth and fast delivery operations.
The Blinkit quick commerce delivery network is designed to be flexible. AI-powered algorithms help predict demand in real time and optimize delivery routes based on factors like traffic, location, and customer preferences. This results in reduced delivery times and greater customer satisfaction.
Expansion Across Product Categories
While Blinkit started by focusing on groceries, it has expanded its offerings to a wide range of products, including general merchandise, electronics, fashion, and personal care items. This category expansion is in line with the growing demand for quick, on-demand shopping across different segments.
As Q-commerce continues to rise, Blinkit is actively tapping into high-demand product categories like electronics, apparel, and home essentials. The company has also embraced trend-first commerce and hyper-value commerce, adapting to rapidly changing consumer preferences and price sensitivity.
Revenue Model Using Commissions, Ads, and Subscriptions
Blinkit’s revenue stream comes from multiple points, including a commission from vendors for each sale made through the platform. The platform partners with local vendors and brands, allowing them to sell their products directly to consumers via the Blinkit platform.
Blinkit charges a delivery fee based on the size of the order and the customer’s location. This fee helps the company cover the cost of transportation and delivery personnel. Blinkit offers a subscription service to customers who wish to access benefits such as free delivery and exclusive discounts. It also uses additional monetization strategies, such as advertising and platform fees.
Expanding Consumer Base Through Convenience
Blinkit’s consumer base is based on, particularly in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities. Three in five new shoppers since 2020 have come from smaller towns, where Blinkit’s model of quick delivery and affordable pricing is gaining traction.
According to a Blinkit report, Q-commerce thrives on the principle of instant gratification, where users prioritize speed and convenience over planned purchases. Most transactions involve last-minute essentials, and if recommended effectively, users are likely to add complementary items to their cart.
Shoppers typically don’t spend much time exploring offers; instead, they quickly add products that are immediately visible and accessible. Blinkit’s quick commerce model is particularly relevant in these markets, where demand for fast, affordable, and reliable delivery is growing.
Integration of AI and Data Analytics
One of the driving forces behind Blinkit’s business model is its integration of AI and data analytics into its operations. By using customer data, Blinkit can predict demand patterns, optimize inventory management, and fine-tune delivery logistics.
Through AI, Blinkit also identifies trends in consumer behavior, allowing it to personalize recommendations for users and enhance the shopping experience. This focus on data-driven decision-making ensures that Blinkit can offer the right products, at the right price, to the right customers, increasing both conversion rates and customer loyalty.
The Role of Quick Commerce Intelligence
As Blinkit continues to evolve in the competitive quick commerce space, staying ahead of the game requires data-driven decision-making. Quick commerce data analytics can play a crucial role in improving Blinkit’s operations and customer experience.
Optimizing Inventory Management
With Blinkit’s rapid delivery promise, inventory management is a critical area in which data analytics can help. Quick commerce intelligence tools allow Blinkit to track product performance in real-time across its dark stores, ensuring that inventory levels are aligned with demand.
By using assortment and availability monitoring software to check stock availability, sales trends, and even competitor activity, Blinkit can ensure that its most popular products are always in stock, reducing stockouts and overstocking.
Enhancing Product Visibility
Product visibility on the digital shelf is key to driving sales for a platform like Blinkit. By using quick commerce intelligence tools, Blinkit can track how its products appear in-app and on search results, ensuring that high-demand items are placed in prime locations.
Quick commerce intelligence tools like MetricsCart also allow Blinkit to monitor competitor listings, enabling it to adapt quickly and remain competitive.
Price Optimization
In the highly competitive world of quick commerce, price sensitivity is a significant factor. Quick commerce data optimization can help Blinkit with its pricing strategy by tracking competitor pricing, customer preferences, and even regional trends. This allows Blinkit to adjust prices dynamically, ensuring that it remains competitive while maximizing margins.
READ MORE | How can sentiment analysis help in understanding customer mindset? Check out our blog on How to Perform Review Sentiment Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide.
Conclusion
As India’s e-retail market continues to expand rapidly, Blinkit’s quick commerce model, coupled with its focus on local inventory management and customer-centric delivery options, has allowed it to carve out a dominant position in the space.
With the rise of Gen Z, who are increasingly relying on quick, impulse-based purchases, and the expanding reach into Tier-2 and smaller cities, Blinkit is perfectly positioned to continue its growth trajectory.
As quick commerce continues to grow and evolve, Blinkit’s ability to adapt its business model, optimize operations with quick commerce intelligence tools like MetricsCart, and cater to the diverse needs of Indian consumers will ensure its continued growth in the rapidly changing Indian e-retail landscape.
Supercharge Your Quick Commerce Strategy Now!
FAQ
Blinkit operates on a hyper-local marketplace model, focusing on the rapid delivery of groceries and essentials from local dark stores and charging delivery fees, commissions, and subscription-based services.
Brands can optimize product titles, images, and metadata using quick commerce intelligence tools. Strategic placements and sponsored listings also help gain visibility, where users make quick decisions.
Competitive pricing is crucial as users make impulse buys. Dynamic pricing based on demand, competitor rates, and local trends can help maintain profitability and attract recurring customers.
Quick commerce data provides real-time insights on product performance, competitor pricing, customer reviews, and availability, enabling brands to optimize listings and stay agile in fast-paced environments.
Using paid promotions, banner placements, in-app advertising, and time-bound discounts can drive visibility. Additionally, aligning with high-demand time slots (like evenings or weekends) boosts conversions.