In 1888, Coca-Cola mailed out thousands of free coupons to customers who could avail of a free glass of Coke. Following this promotion, the same year, on average, the company sold nine glasses of Coke daily. The rest is history!

If brands want to draw customers and earn profits, promotions must be deployed efficiently. Customer price sensitivity is associated with different product categories at various levels.
Let’s explore some popular promotional pricing examples that brands can consider depending on their business goals.
How Does a Promotional Pricing Strategy Work?
Promotional pricing is a strategy where product prices are reduced for the short term to attract new customers and increase sales.
By lowering the price for a short period, a brand increases the perceived value of a product. The limited promotional period and supply scarcity motivate customers to buy the product while it is on sale.
In addition, it encourages cost-sensitive customers who may have yet to purchase the product at full price to buy it before the deal ends. Thus, a promotional pricing strategy can increase revenue, build customer loyalty, and improve short-term cash flow.
Advantages of Promotional Pricing
Promotional pricing offers numerous benefits for brands. They include:
- Boosts sales and generates revenue, especially during slow periods or when introducing a new product
- Helps clear out excess inventory, thus reducing carrying costs and improving cash flow
- Expand client base and improve customer acquisition by attracting price-sensitive customers
- Creates a sense of urgency and customer excitement, leading to increased sales and profitability.
- Helps retain existing customers and stay competitive by recognizing their needs and offering affordable products
10 Types of Promotional Pricing Used by E-Commerce Brands
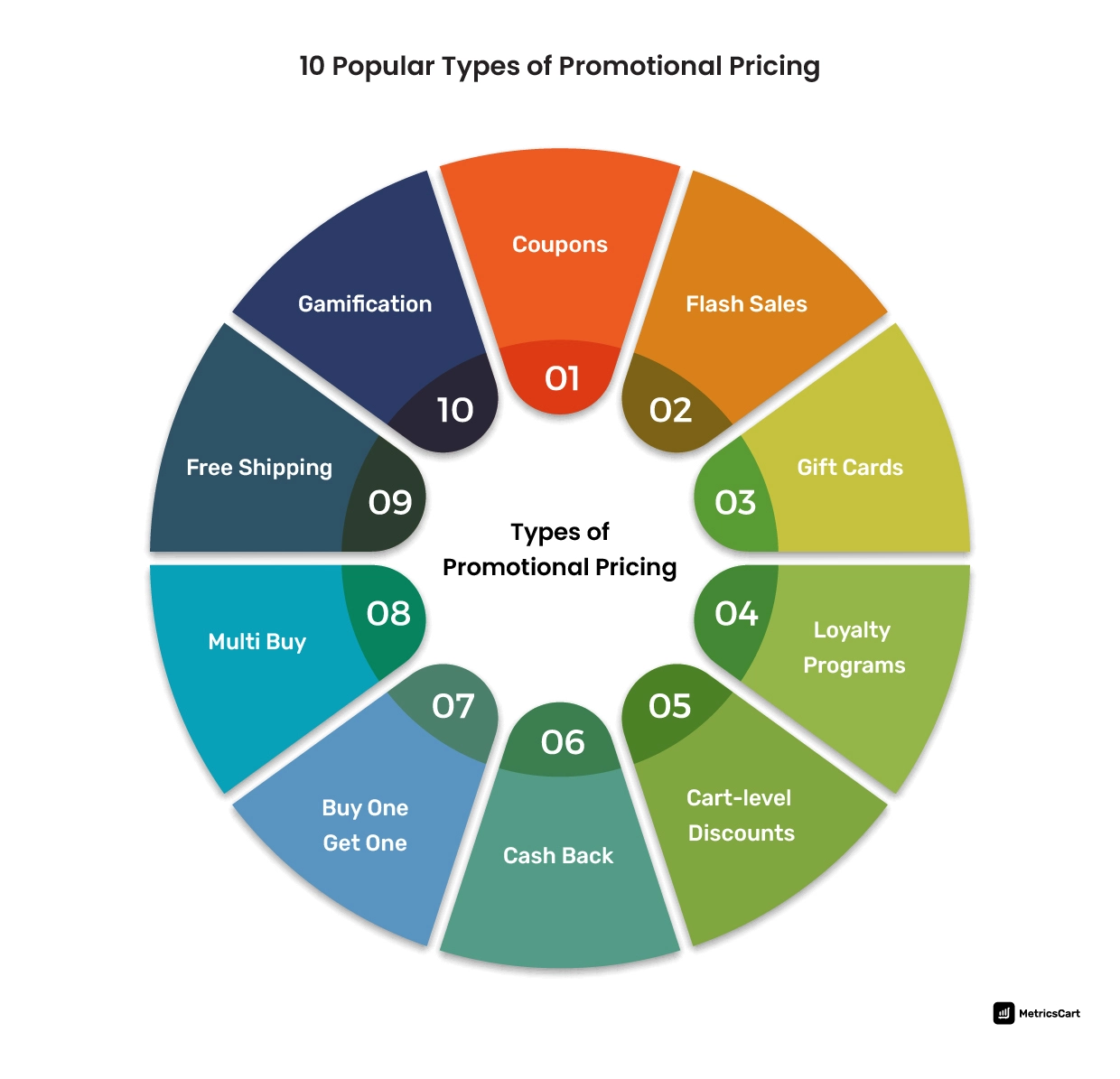
Coupons
The coupon campaign is a versatile medium for promotion. It brings the convenience of an omnichannel experience as the coupons can be used online or in-store. Over 90% of households claimed they had used at least one coupon in the last 12 months.
Some common examples of coupons include:
- New user: WELCOME50 – 50% off on the first purchase.
- Loyal customers: LOYALTY40 – 40% off for loyal customers.
- Inactive customers: BUYAGAIN25 – 25% off on inactive customers’ purchases.
Thus, coupons help brands attract new customers and create repeat sales opportunities.
Flash Sale
A flash sale is when brands or e-commerce platforms offer substantial product discounts within a relatively short time, typically a day or two. There is usually a countdown timer on the homepage or specific words, such as “Hurry! The offer ends at midnight, only for a limited time!”
This leads to impulse buying by creating a sense of urgency and a fear of losing opportunities among shoppers. It is also an effective tactic to unload excess inventory or gain new customers.

For instance, this 24-hour flash sale poster by Forever 21 builds excitement in customers to make purchases quickly. The words ‘gone in 21 seconds’ create a sense of fear of losing out on the opportunity of low prices offered just for a day.
Gift Cards
Gift card campaigns are promotional techniques where brands give (not sell) gift cards to their existing or potential customers. For example, brands send gift cards to customers on special occasions, like birthdays or anniversaries, and seasonal events, such as Valentine’s Day or Christmas.
An example is Target’s themed gift cards. One of the advantages of a Target gift card is that it does not expire nor lose value. Apart from the Target store itself, customers can redeem the gift card at other partner retailers such as Starbucks, Disneyland, REI, Airbnb, and so on.
Loyalty program
A loyalty program is a reward program that incentivizes brand loyalty by offering deals and discounts for customers who make consistent, repeated purchases. Since acquiring a new customer costs more than retaining an existing one, a loyalty program is one of the popular promotional pricing examples.
Sephora’s Beauty Insider is a free-to-join loyalty program for Sephora shoppers in the US and Canada. It offers various deals and discounts a customer can avail if they spend a certain amount per year.
For example, customers who spend $1000 a year can gain rewards like end-of-year discounts, 20% on seasonal savings events, exchange 2,500 points for $100 off purchases, etc.
This will encourage both existing and new customers to make more purchases to gain more bonuses and points for the future.
Cart Level Discounts
Cart level discounts are designed to encourage customers to purchase by providing a specific percentage discount or a fixed amount reduction on their order during checkout. It is usually done when they reach a minimum spending point or buy a combination of products.
Brands can determine cart-level discounts in a timebound manner. It can be Starts on and Expires promotional campaigns where they can mark the period during which customers can avail discounts. Another example would be Valid within a Time Frame where the promotion would run for specific days or hours.
Some common types of in-cart promotions include:
- Abandoned cart promotions: In this method, the retailer sends an email/SMS/push notification offering a discount on the products in their cart. It encourages customers to return and complete their purchases.
- Volume discounts: Here, customers are offered a percentage or a certain amount deduction for their purchase when they spend a specific amount. It increases the average order value and motivates customers to buy more products.
- Referral-oriented cart promotion: It is a combination of cart-level discounts and referral campaigns. The discount is offered to both the referrer and the referred customer as a percentage or fixed amount off their next purchase.
- Product-specific cart promotion: It involves discounts on a specific product or group of products when added to the cart. It helps to increase the number of regular purchases of this specific product.
- Sign-up cart discount: Here, the retailers would initially ask customers to sign up for their newsletter, create an account, or subscribe to their service. Then, they are offered a discount on the first purchase, increasing the customer base.
Free Shipping Promotion
Making free shipping available on all orders for a limited time is a motivation for customers who want to avoid paying for shipping costs. Threshold-free shipping (TFS) policy, where retailers bear the shipping cost for orders exceeding a minimum purchase quantity, is quite popular nowadays.
This offer entices customers to add a few extra items to their shopping cart to reach the minimum purchase, thus increasing the average order value.
For example, Amazon offers unlimited FREE two-day shipping on eligible items with Amazon Prime, with no minimum cost. By offering free shipping, brands can reduce cart abandonment and boost conversion and sales rates.
Cashback
The cashback promotional strategy rewards customers with a certain percentage of their spending as credit for future purchases or direct cash. Cashbacks encourage repeat purchases by rewarding customers after they buy, fostering a sense of accumulation and future gain.
For instance, Target offers the Target Circle program, where members can earn 1% cashback on every eligible purchase, which can be redeemed on future Target purchases.
Buy One, Get One, or Bundle Pricing
The “buy one, get one free” deal is one of the more prominent examples of promotional pricing. It can be applied in various ways:
- Buy one at full price and get one free
- Buy one and get the second item for a specific discount.
When individual products that can be sold separately are sold together to make customers believe they are receiving value, it is called bundling. This tactic helps retailers and brands clear stocks or make customers try a different product from the same brand.

Here is a promotional poster of Dove promoted by CVS Pharmacy. Customers who use Dove soap may find value in this offer as they can try any other Dove product for half-price or get another soap for a 50% discount.
READ MORE | Struggling to execute a successful bundle pricing strategy? Check our Bundle Pricing Explained with Examples
Multi-Buy Promotion
Multi-buy is a variation of bundled pricing that offers a promotion when the customer buys two or more discounted products, like “2 for the price of 1”. This promotion does not add value for customers who need only one unit of an item.
For example, there is an increased demand for candies and chocolates during Halloween. Smith’s store offers Mars and Hershey’s candy bags for an attractive price of $2 each if a customer buys a set of 5 packs.
With this offer price, the retailer expects to sell more volume and clear the shelf of slow-moving items. As a result, a shopper who has never tried brands like Oh Henry! or Almond Joy can try the product at a lower price.
Gamification
Gamification is one of the promotional pricing examples that involves incorporating game-related elements into a non-game environment like e-commerce. Here, customers can play games to earn more reward points, gain badges, or buy new items.
Some common gamification elements in e-commerce are:
- Time-bound challenges to win prizes
- Interactive spinning wheels to get discounts
- Quizzes or questionnaire
- Treasure hunts or scavenger hunts to unlock reward points
These days, premium brands like Prada, Louis Vuitton, Burberry, American Eagle, etc., are using marketing techniques based on gamification to offer discounts without diluting their brand perception.
For instance, Elaine Giselle, a US jewelry brand, uses spin-to-win pop-ups that enable users to win discounts and other prizes.
READ MORE | Want to learn about other e-commerce pricing strategies? Check out Best Pricing Strategies for E-Commerce That Help Scale Business
Final Thoughts
While most brands consider price sensitivity when implementing pricing strategies, they fail to analyze other factors related to customers, competitors, and suppliers. As a result, many promotional strategies do not translate into profit or meet the retailers’ expectations.
Rather than reactively addressing this issue, e-commerce retailers can leverage a suitable price monitoring tool to gain real-time insights and create an optimal pricing and promotional strategy.
Contact us now to design the right promotional pricing strategy for your business.