Top brands and retailers are optimizing SKUs and focusing on best sellers to deliver a customer-centric portfolio.
In the current scenario, with rapidly changing consumer needs, Deloitte’s 2024 Consumer Products Industry Outlook report states that consumer goods companies should cautiously increase the volume of their product portfolio and focus on cost and efficiency to achieve profitable growth.
SKU rationalization is one way companies remove non-valued features from their product portfolio and achieve cost efficiency.
What is SKU Rationalization?
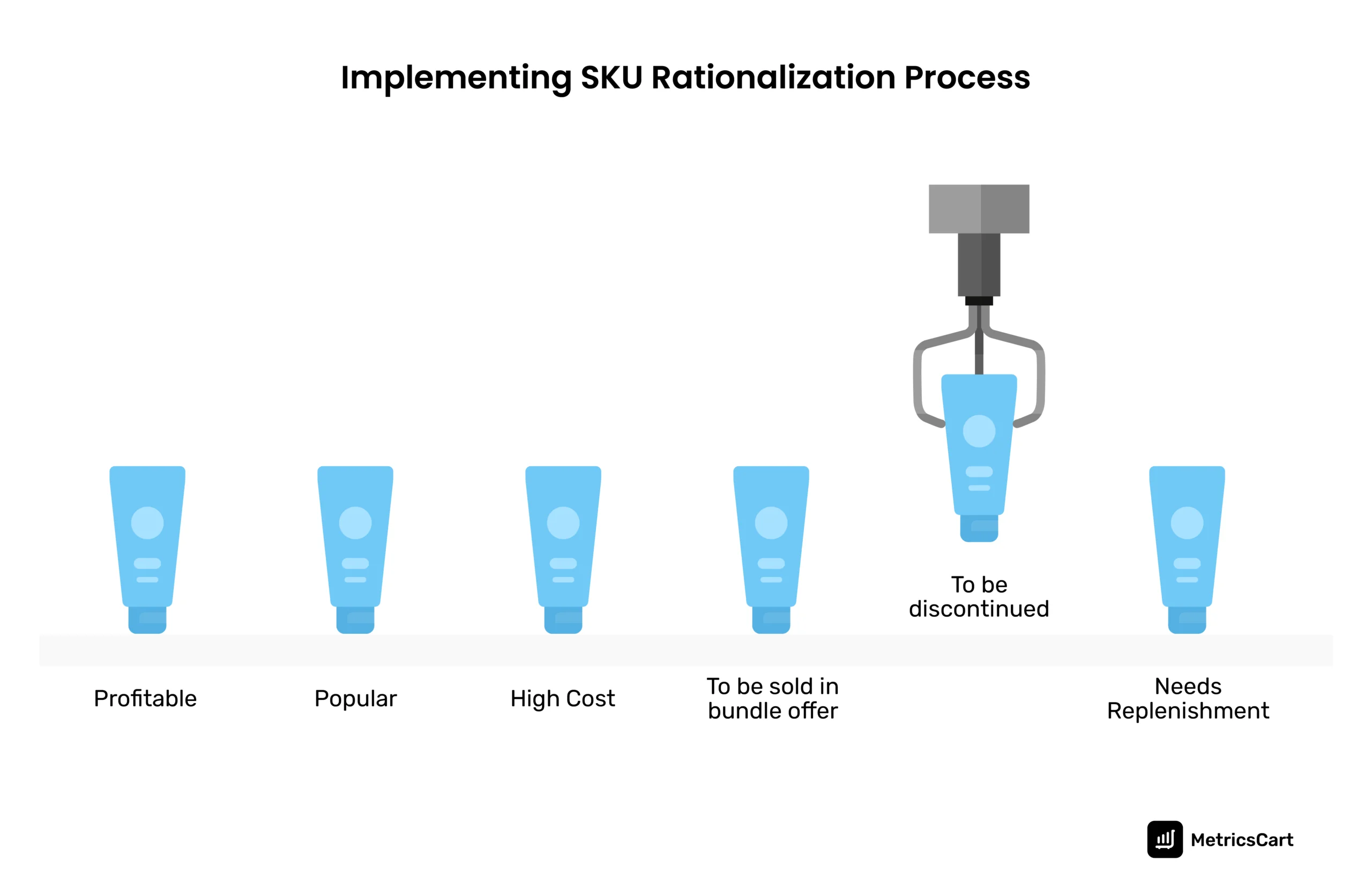
SKU rationalization is the process of determining products to be eliminated or improved based on the analysis of the value addition it provides to the business. Granular-level analysis of various factors about the inventory helps in rationalization.

Through SKU rationalization, brands do a value analysis of their product portfolio and decide on retaining, expanding, reducing, or discontinuing SKUs. Similarly, retailers decide on the optimal product assortment mix in their stores by implementing the SKU rationalization process.
Purpose of SKU Rationalization in Inventory Management
There are several benefits of SKU rationalization. Businesses looking to refresh their product catalog often conduct SKU rationalization to:
- Evaluate the performance and relevance of individual SKUs
- Streamline inventory processes to improve profit margins
- Discontinue non-valued SKUs that reduce the company’s operating efficiency
It is observed that retailers and brand owners who regularly review digital shelves or the product assortment and facings on physical shelves in stores execute better strategies related to pricing, promotion, and product availability.
Impact of SKU Rationalization on the Retail Sector
For customer loyalty, the product mix allocation in a store has to appeal to the shoppers. Therefore, it is challenging for retailers with stores spread out in a country to implement an optimal SKU mix.
Successful retailers conduct extensive market research to understand customer-based preferences before deciding on an assortment strategy and product mix.
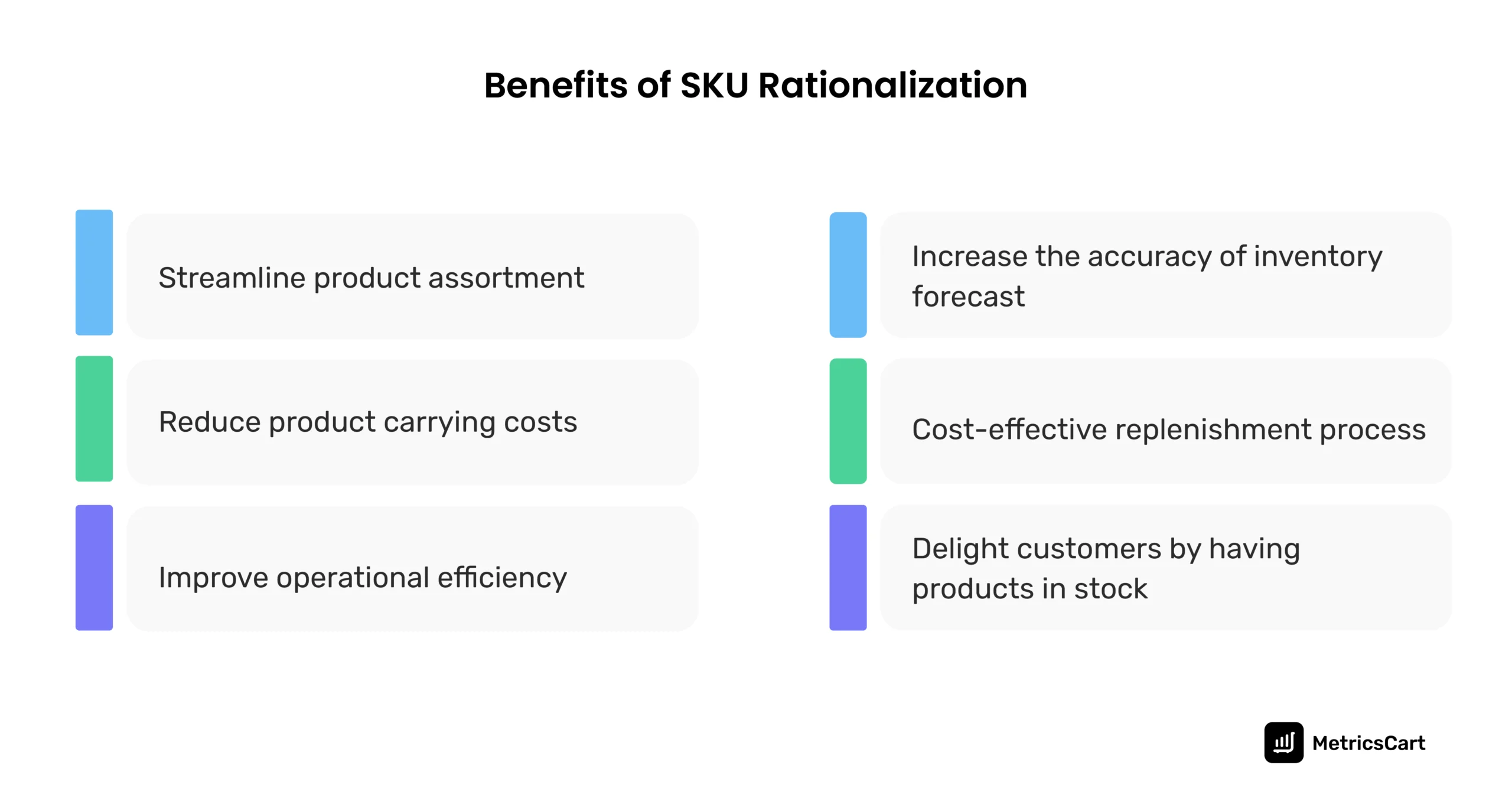
The benefits of rationalizing SKUs for retailers include:
- Trace down inventory irregularities and cost-to-profit ratio
- Reduce carrying costs by discontinuing poorly performing SKUs
- Identify and allocate more resources towards high-performing SKUs
- Assess the impact of private labels in the assortment mix
- Maintain a product assortment as per the demand of customers in a catchment area
- Avoid issues such as stockouts by reordering goods when they are low in stock
- Decide on strategies to enhance competitiveness, operational efficiency, and profitability
According to the 2019 Analytical Assortment Optimization report by McKinsey, accurate inventory management and a streamlined supply chain are the two main elements necessary for e-commerce success.
By implementing SKU rationalization, sellers and brands manage and keep the catalog more organized and up-to-date across all online sales channels.
SKU Rationalization Is Most Prevalent in the Electronic Category
In terms of categories, technological advancements make products in the electronic industry obsolete faster than in other industries. Therefore, almost all retailers selling electronic products use SKU rationalization when new items debut.
To accommodate the latest upgrades and give more focus to high-demand products with higher margins, retailers remove unpopular items from the retail shelves.
Examples of Retailers That Have Benefitted from SKU Rationalization
Dollar General to Perform SKU Rationalization in 2024
The discount store, which has around 10000-12000 SKUs depending on the store format, plans to have a 19% cut in SKUs per store in 2024, especially in the core everyday non-consumable category.
The projected benefits the store is expecting from SKU rationalization are:
- Boost margins
- Reduce the risk of shrink
- Streamline supply chain constraints
- Improve employee engagement with consumers
- With easily manageable SKUs, dedicate more time to detail
SKU Management is Easy for Costco With the Lean Inventory Model
Costco stocks around 4000 fast-moving SKUs per store and around 11,000 SKUs online. To increase their membership count, the average markup on inventory is kept low at 11%.
Costco stocks fewer national brands and has its private label Kirkland in most categories to improve margins. The retailer’s SKU count remains stable, but it eliminates a rotational item that does not hit a certain threshold in a given time. They also keep introducing new items and give a brief 13-week commitment to these products to check customer response.
Outcome of Fewer SKUs
- As Costco procures limited SKUs in huge quantities, suppliers compete to provide them at the best price.
- Having fewer SKUs, a single account manager deals with all the suppliers reducing the complexities in logistics.
- There is a very slim chance of facing the issue of excess inventory
Examples of SKU Rationalization in Consumer Brands
Coca-Cola Company Achieves Revenue Growth By Reducing SKUs
In 2020, Coca-Cola Co. consolidated 17 business units into 9 and discontinued some SKUs.
To appeal to the new generation of consumers, the Coke creations platform introduced the world’s first futuristic flavor to its product portfolio, which was co-created with AI called Y3000 in 2024.
Impact of SKU Rationalization
After the inventory rationalization in 2020, fruit punch, green apple, red apple, wild cherry, and mango were among the few flavors that went missing from the Fanta lineup.
According to James Quincey, CEO, the company has begun achieving the expected revenue growth due to its focus on fewer brands and SKUs.
Mondelez Uses SKU Rationalization to Control Product Cannibalization
In 2020, Mondelez’s product assortment included 150 brands. The company’s many similar products under different brand names affected sales.
65% of Mondelez’s sales came from 20 popular brands like Cadbury, Barni, Clorets, Milka, Oreo, etc. This means the majority of the brands were slow-moving. In this case, such an innovation led to:
- Brand proliferation
- Increased operational costs
- Reduced profit margins
Thus, in 2020, the company discontinued 25% of the SKUs that contributed less than 2% of company sales. Instead, the company launched new products in specific sizes and price points as required by various channels.
Impact of SKU Rationalization
Modelez’s revenue (North American region) grew from $8157 million in 2020 to $11,078 million in 2023.
Nestle Unlocks Growth Through SKU Rationalization
In 2021, Nestle produced 100,000 SKUs. However, only 11% of the total SKUs accounted for 80% of sales. Roughly one-third of the total SKUs accounted for 1% of sales.
The key growth driver brands include Nestle Professional, Purina Petcare, beverages, frozen food, and Starbucks out-of-home solutions.
In 2022, Nestle initiated ‘Project Tasty’ to unlock growth and save costs through SKU rationalization and innovation in its product formulation and packaging. The company:
- Allocated all the resources to better-performing SKUs
- Ensured availability of top-selling products on retail shelves by improving distribution
- Developed differentiated offerings of coffee blends, updated formulations in dairy and pet food, and simplified the supplement formulation to drive market share
Impact of SKU Rationalization
According to Nestle’s financial report published in 2023, the company’s sales in the North American zone rose to $7 billion, 8.6% more than in 2022. Francois Xavier Roger, Nestle’s CFO, said, “In Q1 2023, volume development was impacted by active and deliberate choices to reduce the number of low-growth and low-margin products.”
Steps Involved in the SKU Rationalization Process
According to McKinsey’s Analytical Assortment Optimization report of 2019, assortment optimization is a continuous cycle. Listing and delisting SKUs are not supposed to be solely based on traditional KPIs like total sales. Brands and retailers follow a simple four-step process to optimize SKUs.
Segment Data on Each SKU in the Company’s Product Portfolio
The product portfolio is primarily categorized into product lines, brands in a category, and their SKUs. They are further grouped according to their sales volume and pricing.
Analyze Current SKUs and Archived Sales Data
To identify trends, patterns, and performance of each SKU, retail executives evaluate revenue, profit margin, and production costs to make informed decisions.
Organize Product Catalog Based on the Analysis
SKUs are flagged for potential discontinuation, bundling, or future modification to make them more profitable. Several factors are taken into account before listing and de-listing SKUs. This includes the customer choices and the impact of discontinuing certain SKUs on other products in the portfolio.
Decision-Making Based on Analysis of Inventory Data
After brainstorming, brands and retailers keep, remove, or review SKUs to maximize the profitability of their company.
Moreover, other dimensions, such as economic performance, value to customers, cost, and the SKU’s role in meeting the retailer’s strategic objectives, are also crucial.
Monitoring Inventory with MetricsCart to Rationalize SKU
MetricsCart’s assortment and availability monitoring service makes it easy to do the SKU rationalization process.
We provide data to manage product portfolios efficiently with a real-time peek into the performance of all the listings. We organize data into:
- The SKUs that are adding to excess inventory and impacting profits
- SKUs that are out of stock and need replenishment
- Customer reviews on each SKU to improve product, marketing, and distribution strategies
- SKU tracking both in physical stores and online data
- Category-wise and brand-wise Amazon bestsellers to understand trends
Explore MetricsCart’s services to leverage real-time inventory monitoring service.