Did you know that in 2023, e-retail sales surpassed 5.8 trillion USD worldwide? Yes, you read that right.
Competition is a natural and fundamental aspect of e-commerce. Brands and retailers often resort to aggressive pricing strategies to attract customers. However, this race to the bottom can severely impact profit margins and brand integrity.
To combat this issue, brands need to implement Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) pricing strategies. Establishing MAP pricing is essential, but it is equally important to utilize MAP monitoring software to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
What is MAP Pricing?
The minimum advertised price or MAP pricing is the lowest price at which online retailers can advertise products of a particular brand. It comes in the form of policies enforced by manufacturers.
While retailers are free to sell products at any price they choose, MAP policies establish a minimum price point that helps maintain brand value and protects profit margins.
In the US, a MAP policy is legally binding between manufacturers and retailers. Both parties agree upon it before the products are sourced. It is worth noting that the fine print varies with suppliers.
What Happens if a Retailer Sells Below the MAP Price?
If a retailer advertises a product below the MAP price, brands have the legal right to withdraw their products or even blacklist the manufacturer. They can further restrict future sales and/or refuse to replenish the respective retailer’s inventory.
Moreover, retailers who frequently violate MAP earn a negative reputation within the industry, affecting their relationships with other manufacturers. Therefore, it is ideal to adhere to the stipulated MAP pricing and build lasting relationships with manufacturers.
In the United States, MAP policies are legally authorized. Federal Antitrust Law regulates MAP violations. MAPs regulate advertised pricing instead of the final selling price. Thus, one can expect severe repercussions for advertising below the said MAP.
On the contrary, MAP policies are considered an infringement of European competition laws. In fact, manufacturers will be fined if they enforce MAP policies on retailers.
READ MORE | Interested to Know How Major Brands Prevent MAP Violations? Check out How Brands Manage MAP Violations To Sustain Brand Value?
MSRP Vs. MAP: What is the Difference?
The Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) is the sale price for products recommended by the manufacturer to sellers. It is designed to keep prices at almost the same level, even in different stores. However, it’s not enforceable, and retailers are free to sell the product above or below this price. On the other hand, retailers cannot advertise any product below the MAP price.
MAP is instituted primarily to maintain brand value and preserve retailer margins, whereas MSRP is suggested to standardize retail pricing and provide a baseline for consumers.
READ MORE | Want to Learn More About These Pricing Strategies? Check out MSRP vs. MAP: Understanding Retail Price Terminologies
iMAP vs. MAP: What is the Difference?
Internet Minimum Advertised Price (iMAP) is a version of MAP specifically designed for e-commerce and online retailers. While MAP applies to both online and offline sales, iMAP focuses on the unique challenges of digital marketplaces.
The key difference is that iMAP often includes additional clauses that address the nuances of online selling, such as:
- Restrictions on promotional pricing during specific periods (e.g., Black Friday)
- Monitoring of third-party marketplaces like Amazon or eBay
With iMAP, brands can enforce consistent pricing across all online platforms, ensuring that retailers do not undercut each other in digital spaces where price comparisons are easier.
MAP vs. UPP: What is the Difference?
Unilateral Pricing Policy (UPP) goes beyond MAP by regulating not just the advertised price but also the actual sale price. Under UPP, the manufacturer fixes the cost of their products: resellers cannot sell a product lower than this threshold.
While MAP focuses on maintaining the advertised price, UPP enforces the sale price, giving manufacturers more control over how their products are priced in the market. UPP is typically used for high-end or luxury products where price integrity is critical to the brand’s image.
READ MORE | Interested in Learning the Significance of UPP? Dive into Understanding Unilateral Pricing Policy: Why Is It Crucial for E-Commerce Businesses?
Why do Brands Need MAP Pricing Policy?
Surveys show that prices are one of the most vital factors for consumers when buying from online stores. Online sellers often slash prices to navigate this cutthroat competition in the market.
Without a well-planned MAP pricing policy, you risk having too many unauthorized sellers, inconsistent pricing across marketplaces, and complaints from your retail partners.
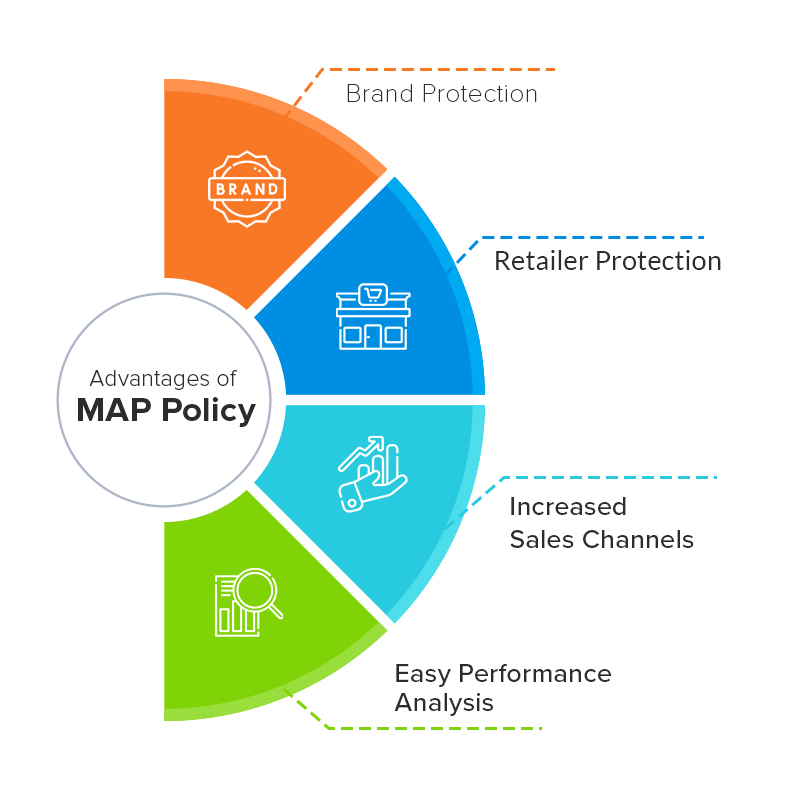
Brand Protection
Without a MAP policy in place, you risk having retailers advertise your products at unreasonably low prices to:
- Enhance in-store footfall
- Increase website traffic
- Clear out product stock
Moreover, marketplaces like Amazon can force sellers to introduce hefty discounts to boost their sales.
In any of the above cases, consumers might perceive your product’s value and brand image as tarnished. By controlling the minimum price at which products can be advertised, brands can prevent price erosion that occurs when retailers engage in aggressive discounting.
Thus, it is recommended that manufacturers retain control over their products through MAP policy.
Retailer Protection
Alongside manufacturers, a MAP policy also ensures the best interests of retailers. When some retailers slash prices to boost sales, others are forced to do the same under competitive pressure, leading to price wars and reduced profit margins. This can reach a point where it doesn’t make any sense for a retailer to stock the respective brand’s products.
Now, a MAP policy restricts the selling behavior of certain retailers, thereby avoiding such situations. This also prevents larger retailers from engaging in predatory pricing tactics—selling products at unsustainably low prices to eliminate competition and monopolize the market. In the long term, it fosters good relationships between retailers and manufacturers.
Increased Sales Channels
MAP compliance protects the interests of any seller, whether retailers or resellers. It helps them believe they can stock your brand’s products without distress and sell them at a competitive price. This can directly increase the number of sales channels your products will be advertised and sold.
Moreover, when brands establish clear pricing guidelines, they can partner with a broader range of retailers without fear of undermining existing relationships or diluting their brand value. It allows you to drive sales and improve customer experience.
Precise Performance Analysis
When all sellers operate within a standard price range under MAP, brands can get an accurate picture of how their products are performing in the market. They can gain real insights into consumer behavior, retailer performance, product performance, and more.
This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making regarding pricing strategies, product positioning, and promotional efforts. Brands can also identify patterns in consumer purchasing behavior linked to pricing changes and adjust their strategy accordingly.
How Do You Create a MAP Policy?
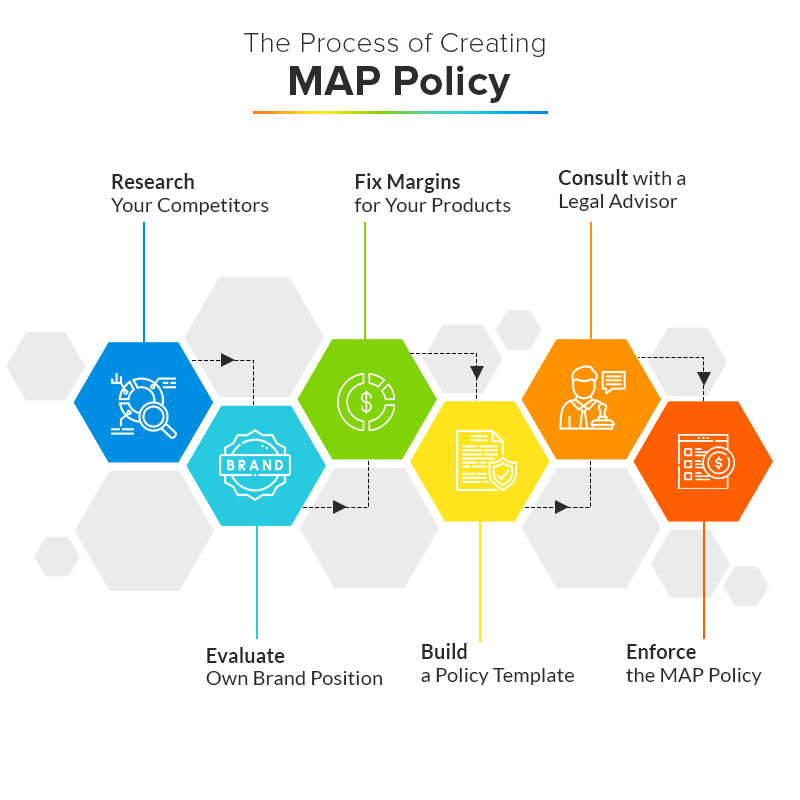
Research and Understand Your Competitors
The first step is to conduct thorough research on your competitors and analyze their pricing strategies for similar products in the market. You can use price monitoring software to analyze your competitors’ price trends and patterns. After this, compare your product’s value proposition against competitors to set a realistic and legally compliant MAP price.
Analyze the Current Brand Position
Next, you need to review historical sales data to understand how price changes have affected sales volume and revenue. Moreover, you should analyze the consumer price sensitivity to determine the optimal pricing range. This will help you choose the appropriate pricing strategy for your products.
Determine Suitable Price Margins
While developing your MAP pricing policy, you need to decide on the appropriate margins, considering factors such as costs, including production, distribution, and marketing, as well as market conditions and changes in consumer behavior that may affect pricing.
You also need to consider whether to allow promotional discounts during special events or sales seasons without violating the MAP.
Create a MAP Policy Template
Once you have completed the first three steps, you need to draft a MAP policy template. It must include specific details about the minimum advertised prices for each product, along with any permitted exceptions. In addition, you must outline penalties for violations, such as warnings, supply suspensions, or removal from authorized retailer lists.
Consult With a Legal Advisor
Before finalizing your MAP policy, consult with a legal advisor who specializes in antitrust law and pricing regulations. This helps avoid potential legal risks, such as price-fixing accusations or anti-competitive behavior. Legal consultation also ensures that your MAP policy is enforceable across different retail channels.
Enforce MAP Pricing Policy
Use MAP monitoring tools to track retailer pricing and detect policy violations across all sales channels. Regularly review retailer advertisements and take swift action against non-compliant sellers. Establish a structured enforcement system, including issuing warnings, restricting supply, or terminating partnerships if necessary.
READ MORE | Struggling to Enforce Your MAP Policy? Check out A Beginner’s Guide to MAP Enforcement in E-Commerce
Conclusion
Establishing and enforcing a Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy is essential for brands looking to protect their reputation and profitability in an increasingly competitive e-commerce environment. By implementing MAP pricing strategies, brands can ensure their products are marketed consistently across all channels while maintaining healthy profit margins.
Contact MetricsCart for further insights into MAP monitoring software that help implement these strategies effectively.
Ready To Take Your Brand Performance to the Next Level?
FAQs
Consequences include loss of product supply, marketing support, and strained relationships with manufacturers.
Brands use MAP monitoring software to track advertised prices across different retailers.
Yes, MAP pricing applies to both online and offline retailers, with iMAP designed specifically for online platforms.