Brands often see unauthorized sellers, marketplace volatility, and MAP policy loopholes as the root cause for price violations. And the immediate measure of action for preventing MAP violations is imposing tighter rules and more monitoring. But this surface-level diagnosis misses a deeper, more common trigger.
Many MAP violations actually start in the supply chain. When inventory is uneven, demand shifts across channels, or retailers face stockouts in one market and excess in another, pricing pressure builds long before it shows up on a product page.
In this article, we break down how supply chain flaws lead to MAP violations, how unauthorized sellers get hold of your inventory, and the best MAP violation prevention techniques.
How does Supply Chain Influence MAP
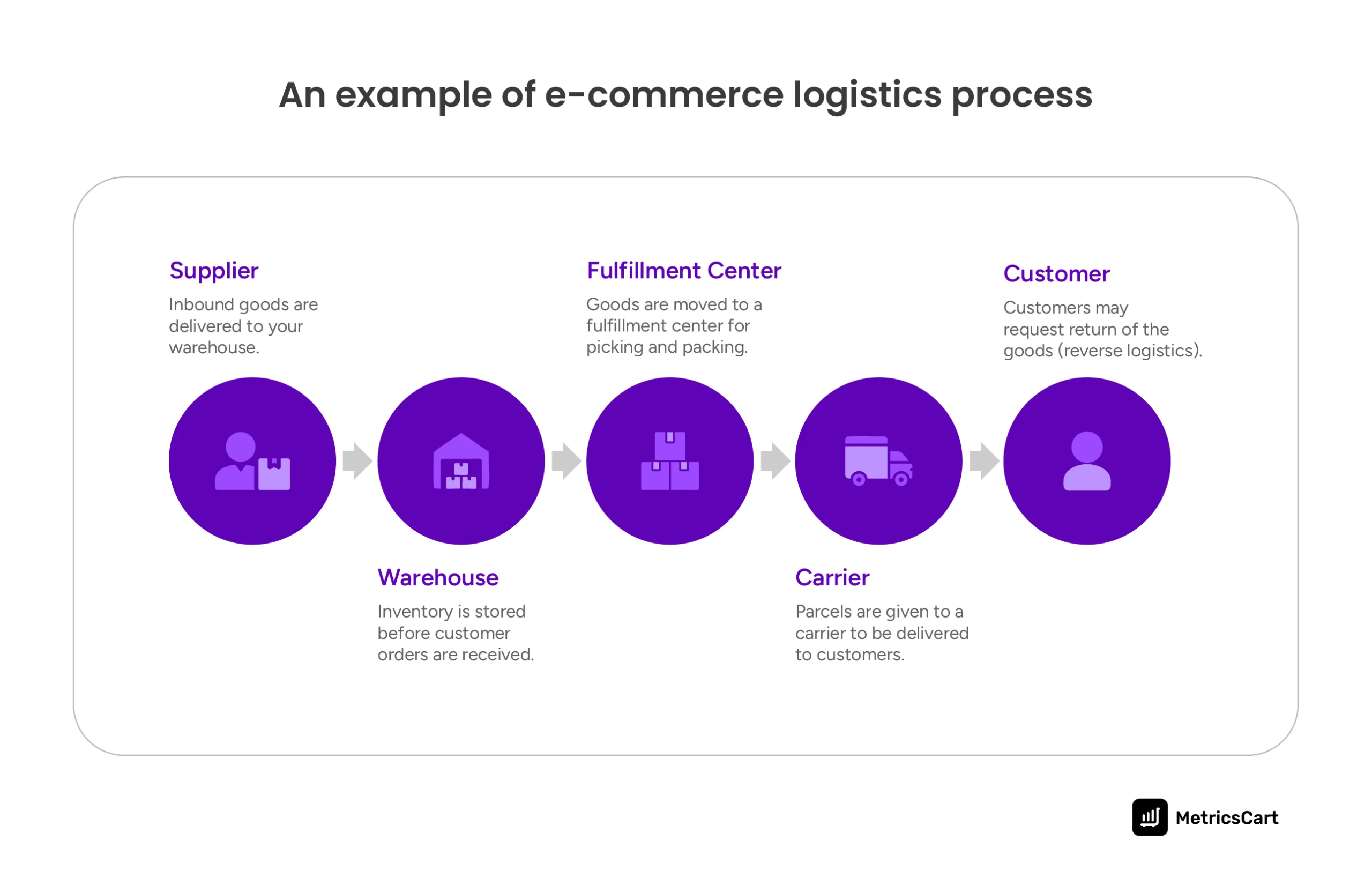
MAP violations may appear online, but many are created much earlier in the supply chain. Every time a product leaves your warehouse, it carries not just your logo, but your price integrity as well. And when that movement isn’t tightly controlled, the pricing you see on marketplaces is simply the downstream effect of upstream gaps.
There are multiple ways supply chain can influence your product’s retail pricing, such as:
Inventory Imbalances and Allocation Gaps
A large share of MAP instability comes from uneven product flow across the supply chain. When some retailers receive too much inventory while others struggle with stockouts, their pricing motivations split immediately.
Overstocked sellers start looking for ways to move product faster, often using quiet discount tactics like coupons, bundled offers, or checkout-based price drops. Meanwhile, retailers facing shortages hold their prices firm, or in some cases raise them to manage demand until replenishment arrives.
This imbalance often results from the bullwhip effect, where small changes in consumer demand trigger larger fluctuations in inventory levels as you move up the supply chain. When retailers increase or decrease orders in response to perceived shifts in demand, suppliers or distributors may overreact, amplifying these fluctuations and causing price pressure that leads to MAP violations.
Distributor-Level Inconsistencies
Who you ship to shapes your entire MAP landscape. When products move through wide or loosely vetted networks, they often reach sellers who have no real incentive to protect your price floor.
Discounting becomes their easiest lever to move volume. And once a few of them start dropping prices, every other seller feels the ripple.
Also, when distributors allocate uneven quantities or offer selective discounts, certain retailers gain better margins or faster access to stock. These advantages translate into more aggressive pricing strategies, while retailers with weaker allocations struggle to stay competitive, sometimes edging dangerously close to MAP thresholds.
Excess Returns and Reverse Logistics Issues
Returned inventory that re-enters the market through liquidators, resellers, or secondary marketplaces is a major MAP disruptor. These units often reach unauthorized sellers with no MAP obligation. Even authorized sellers receiving refurbished or open-box stock may price aggressively to move it.
This fuels a race where clean, full-price inventory gets undercut by products cycling through reverse logistics.
Lack of Traceability
Small operational misses create big MAP issues. Mislabeled SKUs, inconsistent identifiers, changed bundles, or inaccurate records make it hard to track where products actually go. That opens the door to diversion. Items meant for one region show up in another, or stock intended for a specific channel slips into a completely different path. With a broken trail, enforcement becomes guesswork.
For all these reasons, supply chain MAP monitoring becomes just as important as marketplace monitoring.
READ MORE | Role of Customer Feedback in Supply Chain: Why It Matters More Than Ever
How Unauthorized Sellers Get Their Hands on Your Inventory
Lexology reports that 80% of a brand’s price erosion on Amazon is caused by just 20% of unauthorized sellers. These sellers aren’t the result of marketplace chaos; they’re a direct outcome of inventory slipping into the wrong hands. And the root cause is almost always hidden inside everyday supply-chain gaps.
Here are the most common entry points for unauthorized sellers:
- Overstock liquidation: Excess inventory gets cleared through liquidators who resell to anyone, including unauthorized marketplace sellers.
- Distributor dumping: Distributors unload slow-moving or aging stock through unofficial channels to recover cash.
- Untracked sub-distributors: Secondary resellers receive inventory without proper oversight, making it easy for products to move outside your approved network.
- Uncontrolled bulk orders: Large one-off orders go to unvetted buyers who later list the products online at any price.
- Grey-market cross-border movement: Products intended for specific regions are diverted across borders and resold without MAP obligations.
When these pathways stay open, a small group of unauthorized sellers can cause outsized damage to your pricing and brand presence across marketplaces.
READ MORE | How to Monitor and Stop Unauthorized Sellers on Amazon?
How to Build a MAP-Proof Supply Chain
Preventing MAP violations right from the supply chain is not complicated. All you need is complete visibility into who is getting your product, how much they are getting, and what they are allowed to do with it. When those basics are tight, unauthorized sellers lose their access points.
Here is how brands can ensure MAP compliance in the supply chain.
1. Define and Restrict Distributor Roles
Most of the time, MAP violations begin when distributors operate outside the lanes you intended for them to use. Give each distributor clear rules around where they can sell, who they can supply, and how much product they can carry. Tighter roles reduce confusion and stop products from drifting into the wrong hands.
2. Improve SKU-Level Traceability
SKU clarity is the foundation of MAP policy enforcement. When identifiers are mislabeled, duplicated, or inconsistent, products become impossible to track through the system.
So, track products at the SKU level from the moment they leave your warehouse. Knowing exactly which units were shipped, to whom, and when allows you to identify the source of a MAP violation rather than guess.
3. Enforce Bulk-Buy Limits
Large, unmonitored orders are a major source of leakage into discount-heavy channels. A single distributor or reseller buying beyond their typical volume is often the first sign of future MAP instability.
Ensure you have volume thresholds based on historical sell-through rates. It will help prevent stockpiling, behind-the-scenes bulk discounts, and the inevitable sub-MAP clearances that follow.
4. Use Serial Tracking Where Possible
![]()
Serial numbers, QR codes, or unique identifiers help you follow the product through every step of distribution. This makes it much harder for diverted or grey-market goods to blend in and gives you proof when tracking down the source of a leak.
5. Document Every Tier of Resale
Most brands only watch the first tier of distribution. The real problems usually happen in the layers below that. Ask distributors to keep clear records of who they resell to and update those lists regularly. When you know every player in the chain, unauthorized sellers have fewer places to hide.
6. Conduct Routine Supply Chain Audits
Inventory moves quickly, and problems develop quietly. Regular checks on distributor performance, shipment volumes, and geographic patterns can reveal issues early. You often find that a recurring MAP violation stems from predictable, avoidable behavior in the supply chain.
A MAP-proof supply chain isn’t about perfection; it’s about predictability. When product flow is stable, controlled, and traceable, retailers face fewer incentives to discount, distributors avoid channel conflicts, and MAP enforcement becomes dramatically simpler.
Strong Chain, Stronger Brand
A brand’s price integrity is the direct reflection of its operational discipline. When product flow is uneven, or distributors operate without clear boundaries, your pricing floor weakens fast. Simple steps like tightening distributor roles, enforcing bulk-buy limits, and improving SKU-level traceability remove the access points unauthorized sellers rely on. A controlled supply chain makes MAP policy enforcement easier and reduces channel conflict.
Your supply chain is the backbone of your brand. Strengthen it, and your pricing follows. MetricsCart supports this by giving you clear visibility into who is selling your products, how they are priced, and where violations appear. With real-time alerts and marketplace-wide coverage, staying compliant becomes far more manageable.
If you want to safeguard your pricing and protect your brand across all channels, MetricsCart makes it easier to stay ahead.
Stop MAP Violations at the Source with MetricsCart.
FAQs
A MAP violation occurs when a retailer advertises a product below the Minimum Advertised Price set by the brand. This applies to any publicly visible price, including product pages, search results, comparison tables, and promotional ads. A MAP violation can happen even when the final selling price at checkout is different.
Most MAP violations begin with supply-chain leaks such as overstock liquidation, distributor dumping, cross-border diversion, and untracked sub-distributors. When inventory slips into unauthorized hands, sellers have no obligation to respect your price floor. This is why supply chain MAP monitoring is crucial for preventing MAP violations.
Brands can prevent MAP violations by tightening distributor roles, enforcing bulk-buy limits, improving SKU-level traceability, using serial or batch tracking, documenting every tier of resale, and conducting routine supply-chain audits. These steps limit access points for unauthorized sellers.
Strong MAP compliance combines operational control with real-time visibility. Key practices include defining clear MAP terms, limiting backdoor resale paths, using supply chain MAP monitoring tools, capturing evidence for enforcement, and rewarding compliant partners through performance-linked benefits.
MAP violation prevention tools like MetricsCart monitor product listings across marketplaces, detect price drops instantly, identify unknown sellers, track recurring violators, and provide evidence for enforcement. These tools help brands spot issues early and take action before violations spread.