According to a 2023 study by Bankrate, US adults have spent around $71 billion on online impulse buying, which has become an expensive pastime in today’s world.
Consumer online impulse buying has its roots in the psychology of the pleasure principle, but it is not the same as obsessive shopping. It is a ‘spur-of-the-moment’ purchase motivated by multiple factors. It can range from an individual’s mood to the website’s product offerings and pricing strategies.
Types of Impulse Buying
Often celebrated and despised, impulse purchases have occupied a precarious position in the e-commerce industry.
According to motivations and strategies, there are four types of impulse buying:
Pure Impulse Buying
Pure impulse buying is the simplest type of impulse buying, as it relies on an impulsive thought process. The consumer makes the purchasing decision randomly according to their mood or craving. The rationale of budget spending or saving doesn’t apply at this point.
The most common example of this type of impulse buying happens at the checkout line of physical retail stores. To trigger impulse purchases, the shelves near the bill counter are filled with different types of candies, chocolates, mouth fresheners, etc.
READ MORE| Did you know that customer sentiment analysis can help boost customer experience? To know more, check out How Can Sentiment Analysis Help Improve Customer Experience?
Suggestion Impulse Buying
As the name suggests, external factors like mouth-to-mouth opinions, advertisements, etc, motivate this type of impulse purchase. It encourages the consumer to try out new products in the market.
Amazon’s checkout page is an example of this type of purchase. Its algorithm suggests products to buy together with the items in the cart, which triggers an impulse to buy something extra than what the consumer initially plans to shop.
READ MORE| Want to decode consumer behavior on Amazon? Check out Understanding Customer Buying Behavior on Amazon in the US.
Reminder Impulse Buying
In this type of impulse purchase, consumers remember to buy certain items just by browsing through the product list on a website. This happens when a consumer is grocery shopping in an e-commerce store and sees the image of a product.
Online retail stores are different from brick-and-mortar stores in product accessibility and assortment. Hence, the visibility of products on the digital shelf can be a cause of concern. To overcome this, online retailers use strategies like email reminders, push notifications, etc., to remind consumers about products, sales, etc.
READ MORE| How does digital influence impact consumer decisions? To know more, read All You Need to Know About Digital Influence in Retail.
Planned Impulse Buying
Planned impulse buying may sound confusing because it makes no sense. By definition, impulse buying cannot be planned. However, the human mind can be so complex that sometimes certain decisions are planned earlier but executed randomly.
Planned impulse buying happens during product promotions, discount sales, prime-day sales, etc. The consumer has already made a plan to buy an electronic appliance or gadget. But impulse purchase happens when the retailer offers an instant discount for the same product, and the consumer feels the urge to grab the offer.
Why Do Consumers Resort to Impulse Buying?
According to research, impulse buying among consumers happens due to multiple factors; both internal and external.
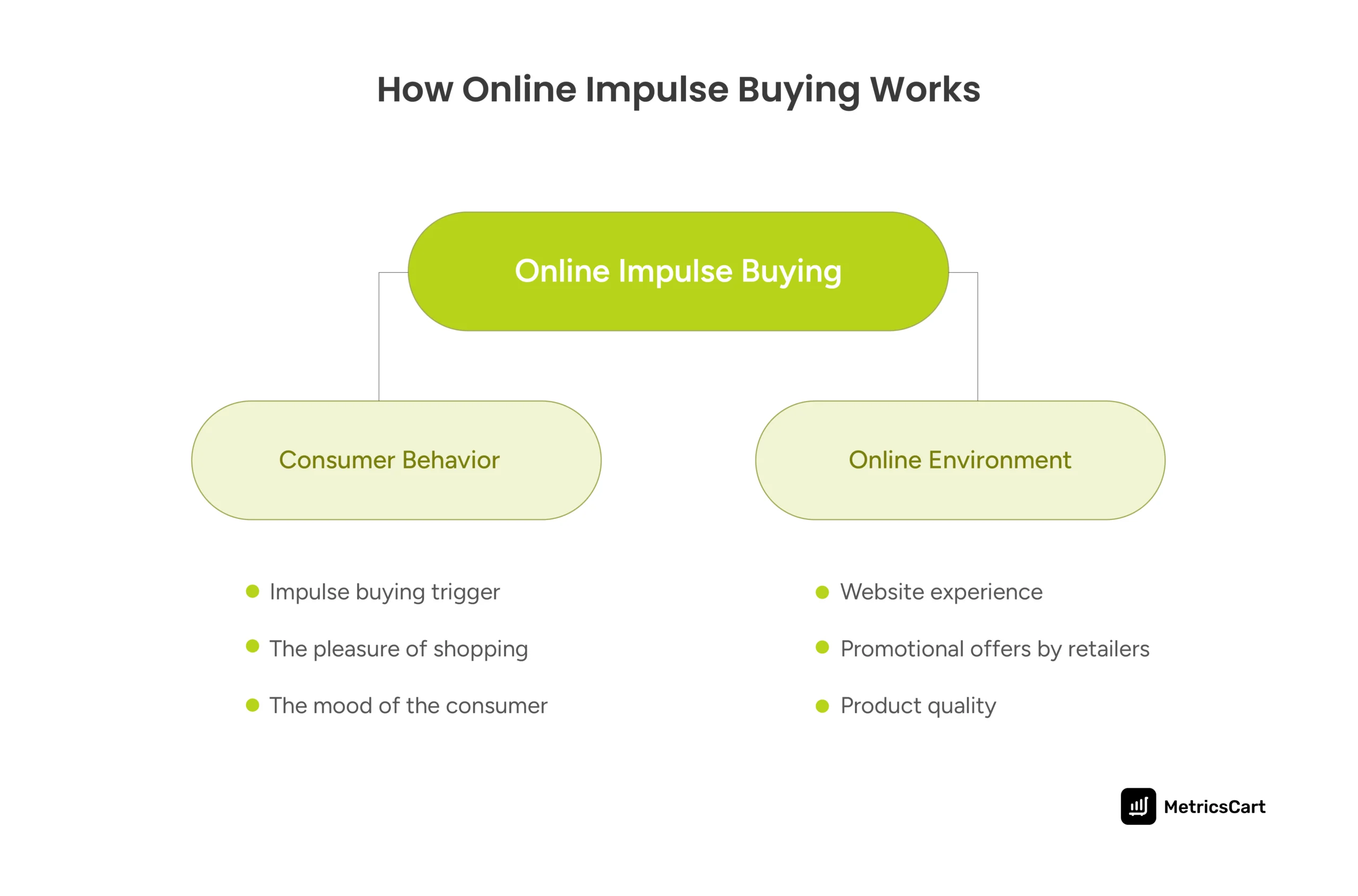
Understanding E-commerce Impulse Buying Through the SOR Model
The Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) model is a key framework for analyzing impulsive buying e-commerce behavior.
- Stimulus refers to both internal factors (like a consumer’s mood or excitement) and external ones (like flash sales, product visuals, or influencer posts).
- Organism represents the consumer’s psychological processing, how they perceive trust, value, and social cues.
- Response is the final action: the impulse purchase.
This model helps brands map out how different online elements, such as urgency tags, user-generated content, and social validation, trigger buying behavior.
Some of the main stimuli for impulse buying in e-commerce are:
Retail Therapy and Emotions
Humans are emotional beings, and their decision-making can vary between emotional and rational reasoning. Retail therapy is a phenomenon in which individuals feel a therapeutic effect while shopping. It gives the consumers a dopamine rush that elevates their mood, making them happy and satisfied.
The rise of social commerce, where buying decisions are heavily influenced by social interactions on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook, has dramatically increased impulsive buying behaviour in e-commerce.
Brands need to recognize that a significant share of their sales may now come from these split-second retail therapy decisions made in emotionally charged environments.
Advertisements, Deals, and Discounts
Retailers often use marketing and pricing strategies like attractive ads, flat discounts, express deals, etc., to lure consumers into buying more products. Impulse buying is a huge plus for retailers, as it motivates consumers to try out new products and increase their buying power.
Research suggests that perceived trust is a major moderator in e-commerce impulse buying. If consumers trust the seller, platform, or product reviews, they are more likely to act on impulse.
This makes credibility indicators such as verified reviews, secure checkout badges, return guarantees, and transparent product information critical. Brands looking to boost impulse sales should invest in building trust-based signals directly into their digital shelf.
Promotional pricing strategy can be used to improve consumer engagement with new and existing products offered by brands.
Peer Pressure and Other External Factors
Societal expectations and peer pressure often affect a consumer’s decision-making. The fear of being left out because one does not own a particular product is considered one of the fundamental reasons for impulse buying.
This type of spending can range from owning a particular model smartphone to bigger purchases like designer clothes, luxury cars, real estate, etc.
COVID-19: The Harbinger of Impulse Purchases
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic created a lot of confusion and fear in consumers, leading to a steep increase in impulse buying through online stores.
According to the survey done in September 2020 by MagnifyMoney, 61% of 1,052 Americans made an impulse purchase in the previous month during the COVID lockdown.
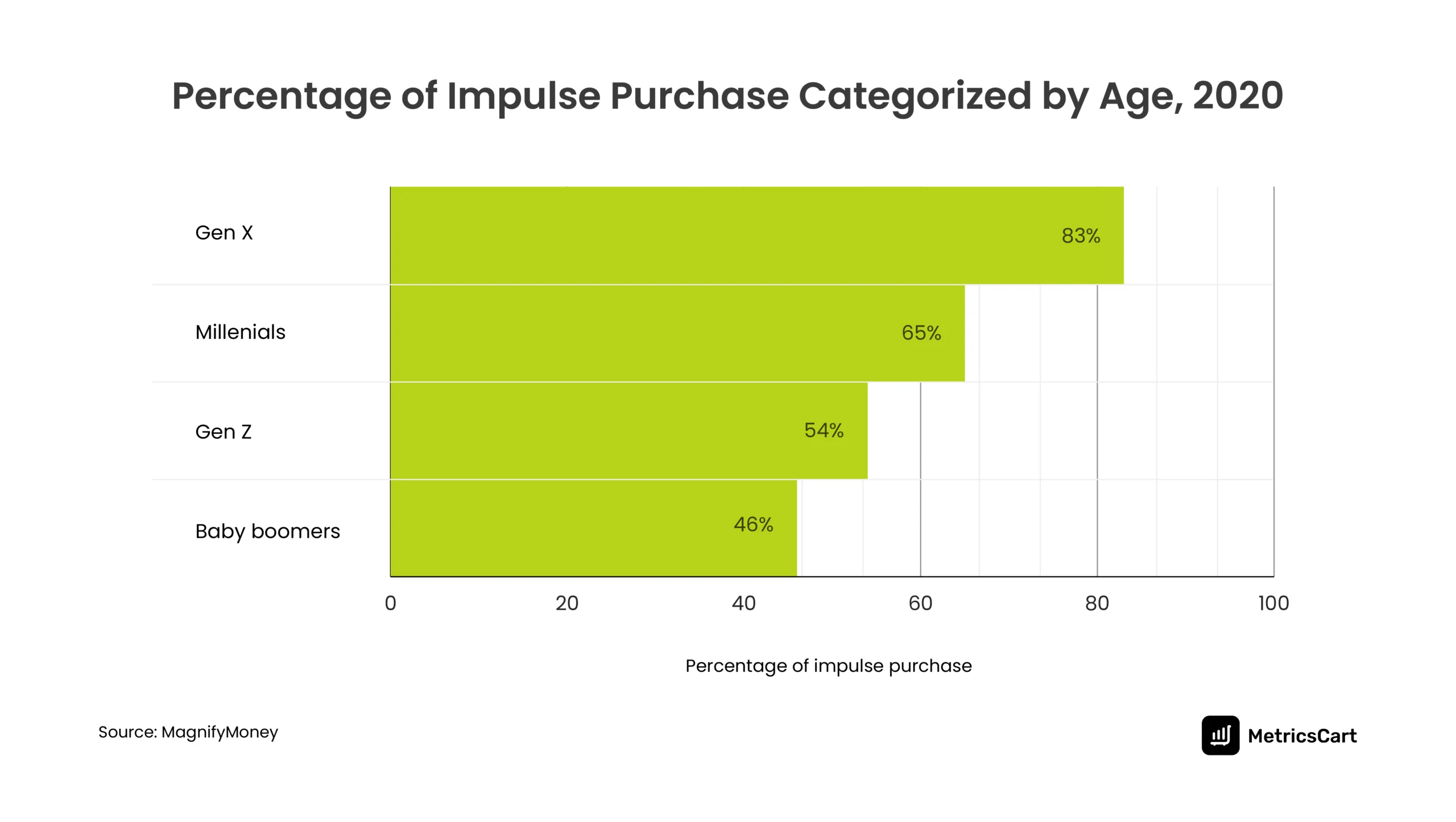
The younger generation belonging to GenX made the most impulse purchases at 83% during this period. However, Millennials spend the highest average amount on impulse purchases at $374.
Also, most impulse purchases were made on groceries, alcohol, coffee, face masks, and sanitizers, respectively.
The pandemic-induced impulse buying in e-commerce was mainly seen as a form of retail therapy, as consumers were stuck at home. Some people lost their jobs, and others were anxious about the future. The shopping experience during COVID-19 gave them a sense of happiness and comfort.
Post-Covid: US Inflation and Impulse Buying Patterns
A 2023 survey commissioned by Slickdeals and conducted by OnePoll states that 48% out of 2000 Americans have reduced their impulse buying. 72% reported inflation as the main reason for reducing impulse shopping.
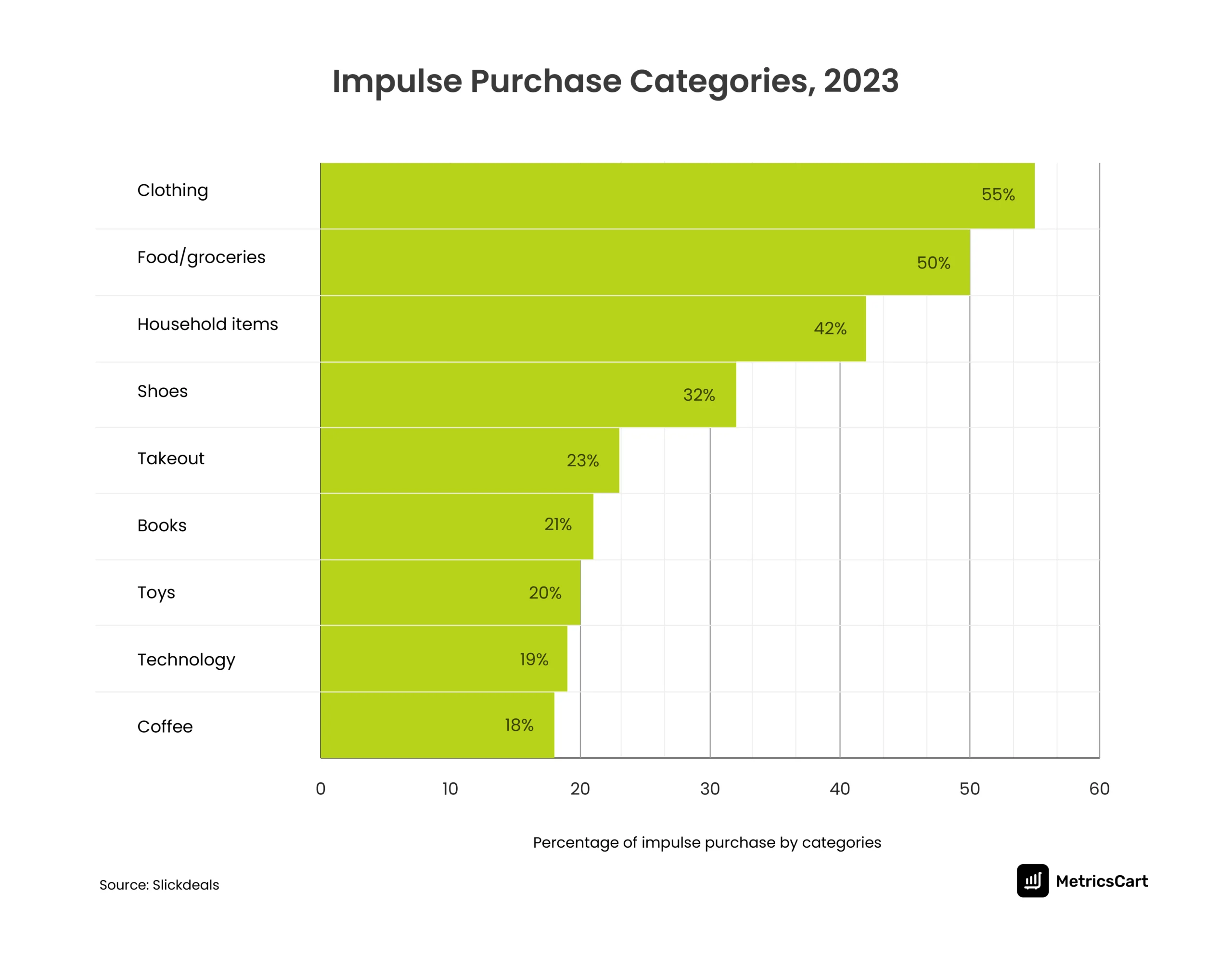
Consumers are becoming more aware of their monthly budget spending and are choosing to spend more on necessities than luxuries. Apparel, groceries and household stood out as the top categories of impulsive shopping. The same survey also observed that the average impulse buying per consumer has come down to just six times per month compared to 12 during 2022 and 2021.
Impulse Buying: A Retailer’s Perspective
On the one hand, an e-commerce platform offers consumers the chance to carefully plan and fill e-carts according to their monthly budget. But on the other hand, social media and hyper-personalized ads encourage consumers to make more impulse purchases.
Bankrate’s survey reports that impulse buying through social media has been on a constant rise, with two in five social media users making an impulse purchase. Millennials spend the highest on impulse purchases, over $1000. Gen Z quickly follows with an average of $850.
Strategies To Boost Online Impulse Purchase
E-commerce businesses employ various strategies to increase online impulse buying, such as:
Website Experience
A seamless and secure website will provide confidence to the consumers for shopping to their heart’s content. This can positively affect impulse buying behavior.
Social Media Influencers
Online businesses use social media influencers to advertise and endorse their products. This strategy works like mouth-to-mouth marketing, as the consumer tends to perceive it as a valuable personal opinion.
Banner Ads
Banner ads on websites and retail apps help to attract the attention of consumers toward a discount sale or a limited-time deal offered by brands or retailers. These ads work like a reminder or suggestion to make an impulse purchase.
Push Notifications
Smartphones and push notifications are inseparable. Push notifications allow online stores to alert consumers of regular offers and other attractive deals. This ensures that the consumers are in the loop and motivates them to make a purchase.
Hyper-Personalized Ads
Localization has become the buzzword in online marketing and sales. Retailers like Amazon use consumer data to create highly personalized product recommendations based on past shopping, search history, real-time data, etc.
Hyper-Targeted Advertisement
Every e-commerce business must target the ideal consumer base to boost sales and revenue. Hyper-targeted marketing allows online businesses to send highly personalized messages to consumers. McDonald’s, Macy’s, Starbucks, etc., utilize location-based marketing and geofencing to deliver personalized product recommendations.
Free and Fast Shipping
According to a 2024 study by Baymard, 48% of US adults abandon their carts due to high shipping costs. So, ensuring cheaper and faster shipping can increase online impulse purchase frequency.
With all these strategies in place, online shopping can still be a daunting experience for consumers. Scams targeted through social media and online payment concerns create red flags that prevent impulse shopping from being instinctual and stress-free like in a brick-and-mortar store.
Conclusion: Impulse Buying and Price Monitoring
It is important to know that impulse buying behavior is unpredictable, and there are no sure-shot techniques for success. However, attractive pricing strategies can help online brands and retailers increase customer loyalty and average order value.
MetricsCart provides you with real-time pricing insights, MAP monitoring, competitor analysis, and review monitoring system to understand how consumers react to your price points. We help you fine-tune pricing strategies, uncover what drives impulse buys, and stay ahead of competitor moves across channels. Optimize with actionable strategies, relevant industry data, and insights to win the shelf.
Ready To Take Control of Your Brand Performance? Strategize With Our Digital Shelf Solutions!
FAQs
Impulse buying is driven by the desire for instant gratification. It is rooted in the psychology of the pleasure principle and is triggered by emotions or cues like sales, scarcity, and attractive displays.
Scarcity, social proof, emotions, and visual appeal are key triggers. Limited offers create a sense of urgency, while emotional states and visually appealing elements prompt quick decisions.
Positive moods increase spending, while negative moods lead to purchases for mood repair. Dopamine release reinforces the behavior, letting the shopper feel a therapeutic effect, and this phenomenon is called retail therapy.
Key factors include motivation, perception, learning, beliefs, attitudes, and personality. These shape how and why consumers choose products.
Yes, social influence strongly impacts online impulse buying. Reviews, ratings, influencer posts, and “trending” labels create pressure to conform, triggering fast, unplanned purchases.